Despite how Ross’ paleontology career is treated by his companions in Friends, there’s something special about finding the remains of creatures that lived millions if not billions of years before us. In fact, humanity’s interest in paleontology isn’t a modern development. Ancient Romans were just as fascinated by fossils.
According to the ancient Roman historian Suetonius, Emperor Augustus established the first known paleontological museum at his villa on the island of Capri, where he showcased the bones of ancient “giants” and “monsters.” While paleontologists have yet to uncover such fantastical remains, a study published Thursday in the journal Science describes something that, in my opinion, is even more special—an ancient Roman amulet crafted from the fossil of a critter that lived between 453 and 460 million years ago.
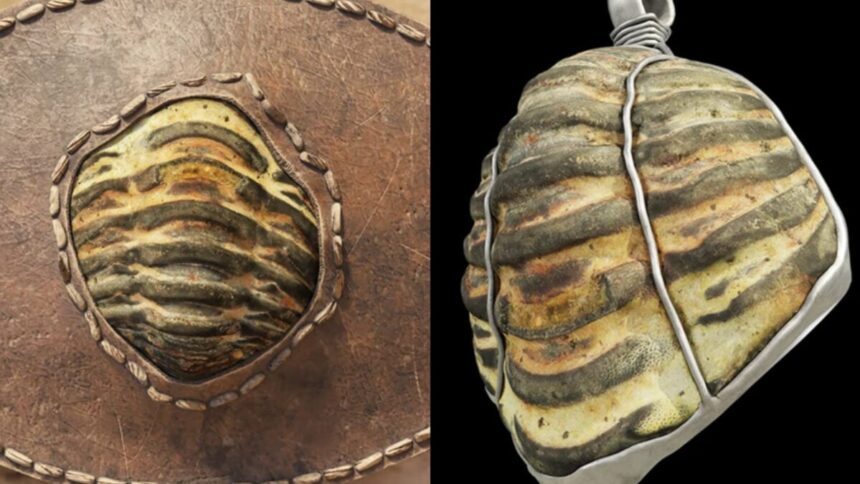
The researchers claim that the artifact “represents the first documented trilobite in the Roman world and the earliest known reference to this fossil group—and the intentional manipulation of a trilobite specimen—in all of classical antiquity,” they wrote in the study. Trilobites are a group of marine arthropods that existed between 521 and 251 million years ago. It’s also the “third trilobite in the global archaeological record to have been collected and used by people over a thousand years ago,” they added.
The rare artifact came to light in a Roman settlement in northwestern Spain called A Cibdá of Armea that existed from the first to the third century CE. The researchers suggest that the fossil itself originated in shale outcrops over 267 miles (430 kilometers) away from the Roman settlement. The trilobite likely reached the settlement via trade or as the property of someone from central Lusitania (a Roman province in Spain) moving to the region.
Either way, someone clearly altered the fossil. “The Armea trilobite fragment unquestionably shows evidence of anthropic work, particularly on the underside and left side of the piece,” the researchers explained. “These marks do not affect the upper surface, which displays the characteristic articulated segments of a trilobite’s dorsal exoskeleton. It seems clear that the person who modified the stone intended to leave that natural surface untouched, while simultaneously adapting the fossil to its new function.”
According to the study, the modified fossil could have functioned as a game token, a part of a necklace or bracelet, a banded pendant on a metallic mount, or simply an object people carried in their bag or pocket. Regardless of how the trilobite was fashioned, it was likely kept for supernatural, propitiatory, or medicinal purposes and abandoned between the first and third centuries CE.
“It is plausible to consider that the Armea trilobite may have been perceived to hold magical and protective powers for its wearer, as is the case with fossils or even trilobites in other well-known archaeological contexts,” the researchers wrote. Coincidentally, archaeologists found the trilobite next to a bronze coin of Augustus.
The discovery is a testament to the fact that humanity’s curiosity for that which came before us is a universal trait that transcends cultures, borders, and even time itself. It stands as a reassuring reminder, especially in times like these—when the only thing everyone seems to agree on is our many differences.
Read the full article here