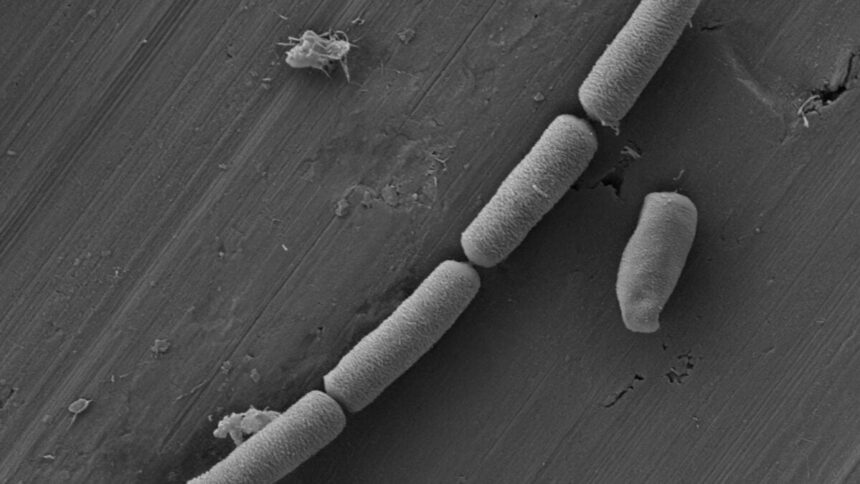
Microbes are known for their remarkable survival abilities. And now, scientists have discovered another remarkable trait: Turning cement into an electricity storage device.
In a study published September 9 in Cell Reports Physical Science, researchers at Aarhus University in Denmark describe how they seeded a bacteria called Shewanella oneidensis into cement. These particular bacteria are known to be good at transferring electrons across surfaces, and the researchers wondered if they could act as an energy transporter in cement.
Indeed, the cement came to life, with the bacteria establishing a “network of charge carriers capable of both storing and releasing electrical energy,” the researchers explained in a statement. In other words, the cement could store and release electricity, a finding that could one day enable more sustainable buildings. Even better, the researchers found that even after the microbes died, the material could be reinvigorated by being fed nutrients.
An undead cement complex
When the microbes inevitably died, a simple trick literally brought them back to life. The team integrated a microfluidic network to supply the bacteria with nutrients, and the same channels could be used to “reawaken” the system, recovering up to 80% of the original energy capacity, according to the study.
“We’ve combined structure with function,” Qi Luo, study lead author and a civil engineer at Aarhus University, said.
“The result is a new kind of material that can both bear loads and store energy—and which is capable of regaining its performance when supplied with nutrients.”
The resulting material produces a hefty load of energy, the researchers said—even under stress. For instance, one stress test involved putting the cement in extreme temperature environments, which it endured with ease. And when the researchers connected six blocks of the cement, the structure generated enough power to switch on an LED light.
The future of sustainable building?
Cement is relatively cheap compared to most materials, making it easy to scale. The bacteria are also abundant in nature, meaning that the technology is sustainable at its core. That said, more work is needed to take what is a proof-of-concept paper through to being a market-ready material.
“We envision this technology being integrated into real buildings, in walls, foundations, or bridges, where it can support renewable energy sources like solar panels by providing local energy storage,” Luo said.
“Imagine a regular room built with bacteria-infused cement: even at a modest energy density of 5 Wh/kg, the walls alone could store about 10 kWh—enough to keep a standard enterprise server running for a whole day.”
Read the full article here