From our cell phones to our smartwatches and laptops, we’re surrounded by battery-powered devices. Today, batteries are solid, voluminous components of our technology—but what if they could be malleable, flexible, and even printable?
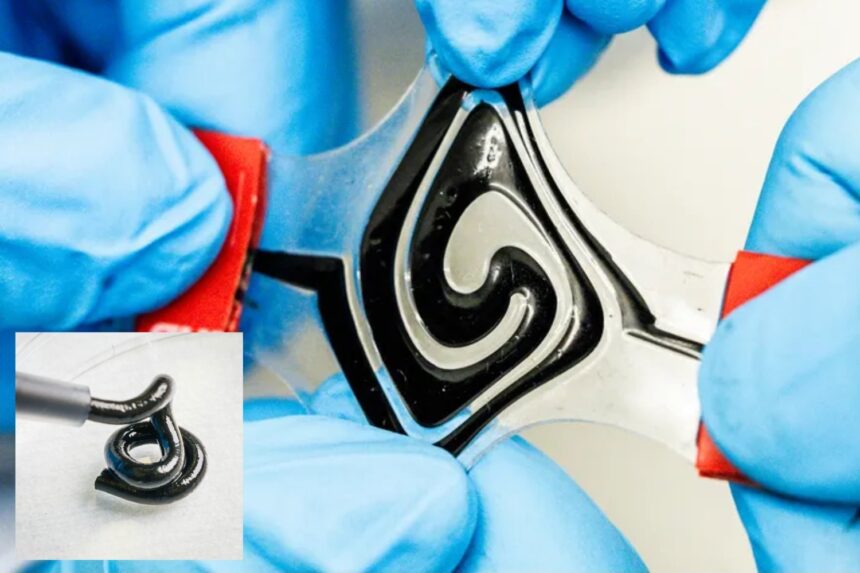
Embracing this idea, researchers in Sweden have developed a fluid battery that can be shaped into different forms. As detailed in a study published April 11 in the journal Science, the battery makes use of electrodes—key conductive materials in batteries—in fluid form. The novel soft structure paves the way for innovative designs of future battery-powered technology.
“Batteries are the largest component of all electronics. Today they are solid and quite bulky. But with a soft and conformable battery, there are no design limitations. It can be integrated into electronics in a completely different way and adapted to the user,” Aiman Rahmanudin, a co-author of the study, said in a university statement. “The texture is a bit like toothpaste. The material can, for instance, be used in a 3D printer to shape the battery as you please.”
According to the statement, previous attempts to achieve soft, stretchable batteries relied on mechanical features like sliding connections or required rare materials that are environmentally harmful to process. The key to Rahmanudin and his colleagues’ success was converting electrodes into a liquid form.
To understand the significance of this achievement, it’s important to remember how batteries actually work. Simply put, an electrochemical battery consists of two different metals, or electrodes: an anode and a cathode. A chemical reaction causes electrons to flow from the anode to the cathode—a process we call electricity—which can do work as it moves, like powering a lightbulb or a device. Larger batteries have greater electrical capacity, but also thicker—and hence more rigid—electrodes.
“We’re the first to show that capacity is independent of rigidity,” said Rahmanudin, who is also a research leader at Linköping University’s Soft Electronics Group at the Laboratory of Organic Electronics.
Prior attempts at developing fluid electrodes relied on liquid metals that sometimes solidified, according to the statement. To bypass these issues, the team used plastics capable of conducting electricity—called conjugated polymers—and lignin, a waste product in paper production. The resulting battery can be recharged over 500 times, even when stretched to twice its original length.
Furthermore, “since the materials in the battery are conjugated polymers and lignin, the raw materials are abundant. By repurposing a byproduct like lignin into a high value commodity such as a battery material we contribute to a more circular model. So, it’s a sustainable alternative,” says Mohsen Mohammadi, a lead author of the study and postdoctoral fellow at Linköping University’s Laboratory of Organic Electronics. Moving forward, the team hopes to improve the battery’s electrical voltage.
“We have shown that the concept works but the performance needs to be improved. The voltage is currently 0.9 volts,” Rahmanudin explained. For comparison, standard AA batteries are between 1.2 and 1.5 volts, and most smartphones operate at between 3.7 and 4.2 volts. “So now we’ll look at using other chemical compounds to increase the voltage.”
By quite literally breaking the mold, the study opens the door to a whole new realm of design possibilities for battery-powered devices.
Read the full article here