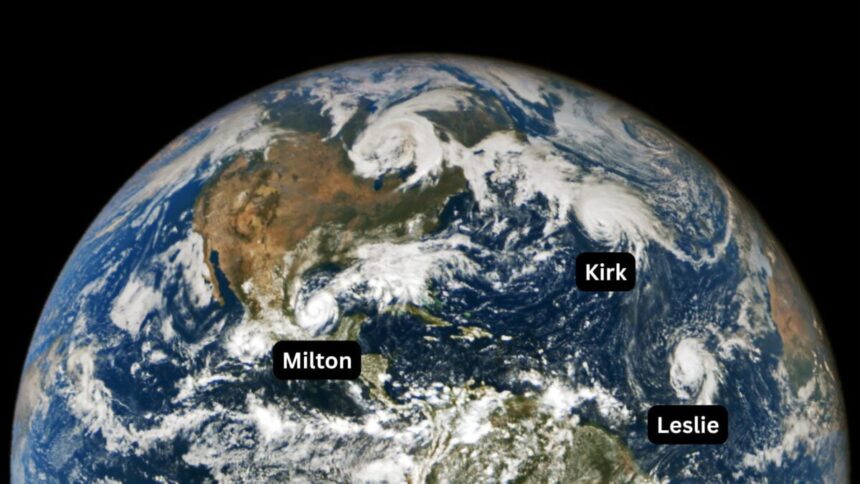
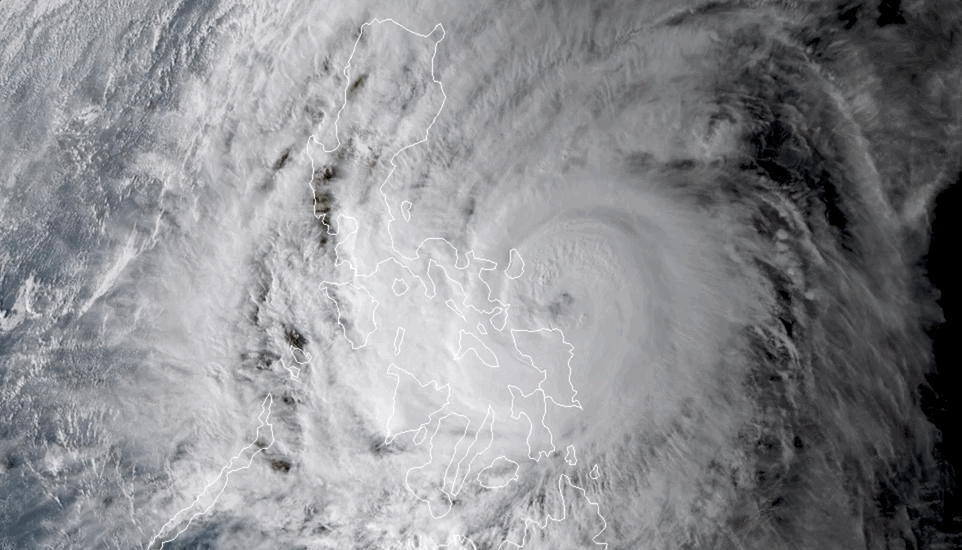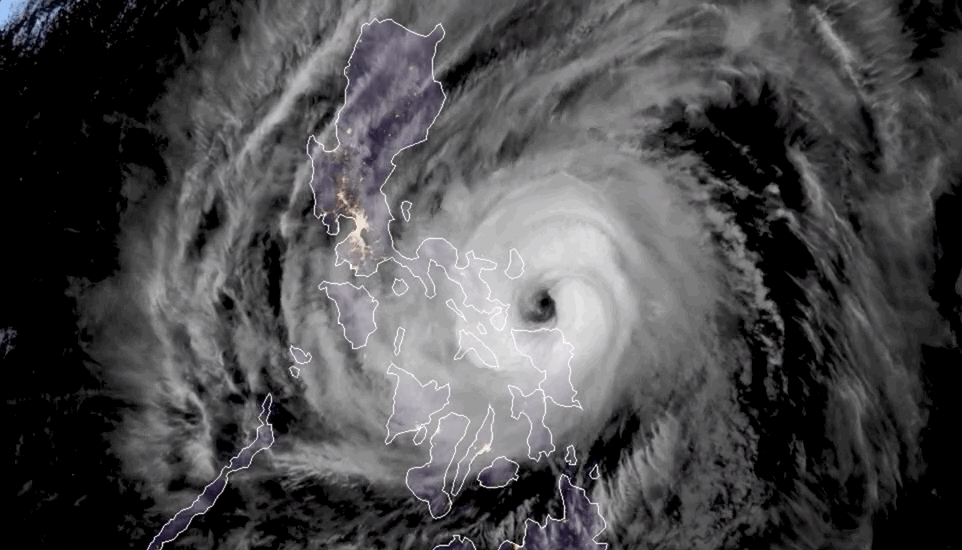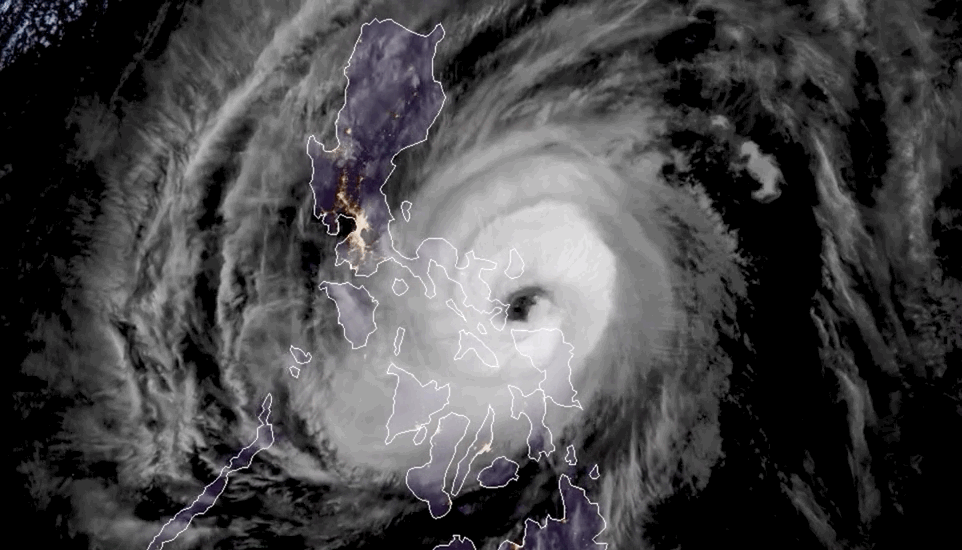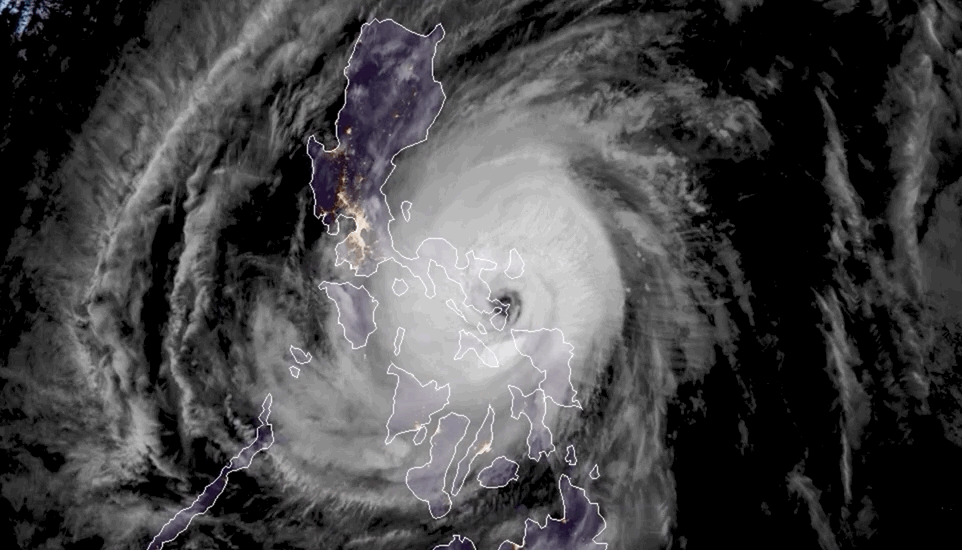
In early October 2024, hurricanes Milton, Kirk, and Leslie churned in the Atlantic Basin—the first time on record that three Atlantic hurricanes were simultaneously active after September, according to NOAA. New research warns that tropical cyclone “clusters” are becoming more common in this part of the world, compounding the hazards of hurricane season.
Tropical cyclone clusters occur when two or more hurricanes are active within the same basin at the same time. The western North Pacific has historically produced the most clusters, but climate change appears to have shifted this hotspot to the North Atlantic. The study, published July 31 in the journal Nature Climate Change, identified a tenfold increase in the likelihood of tropical cyclone cluster formation in the North Atlantic, from about 1.4% to 14.3% over the past 46 years. This rate now surpasses that of the western North Pacific, the researchers state.
“We tried to develop a probabilistic framework to understand this trend,” said Dazhi Xi, a climatologist at the University of Hong Kong who co-led the study and developed the methodology, in a Fudan University release. “If tropical cyclone clusters are formed by chance, then only storm frequency, storm duration, and storm seasonality can impact the chance.”
To rule this out, Xi and his colleagues simulated the formation of tropical cyclone clusters by probabilistic modeling, considering only those three mechanisms. This model was only partly successful—it significantly underestimated the chance of tropical cyclone clusters for some years. The researchers found that during those years, synoptic-scale waves—large, moving atmospheric disturbances that can create conditions conducive for storm formation—increase the odds of tropical cyclone clusters.
Further analysis revealed that the observed changes in synoptic-scale wave intensity are responses to a “La Niña-like” global warming pattern, according to the study. This trend is characterized by slower warming in the Eastern Pacific compared to the Western Pacific.
“The warming pattern not only modulates the frequency of tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic and northwestern Pacific basins, but also impacts the strength of the synoptic-scale waves, together causing the shift of tropical cyclone cluster hotspot from northwestern Pacific to North Atlantic basin,” explained Zheng-Hang Fu, a PhD student at Fudan University who co-led the study, in the release.
It’s unclear whether this warming pattern has resulted from natural variations within the climate system or external pressures, such as greenhouse gas emissions, according to the study. Previous research by Xi found that the future likelihood of multiple hurricanes impacting the same area within a short time period increased in both moderate and high greenhouse gas emissions scenarios, suggesting that human-driven global warming influences simultaneous storm formation.
Though this new study did not look specifically at anthropogenic warming, it suggests that a dramatic shift in warming patterns over the last half century has transformed the North Atlantic into an emerging hotspot for tropical cyclone clusters. This may compound hazards for Atlantic coastal nations during hurricane season, including the U.S.
When multiple hurricanes hit within a short time period, this drastically decreases recovery time between storms, overwhelming emergency response systems and further damaging compromised infrastructure. The researchers hope their findings will urge Atlantic coastal communities to develop proactive strategies to deal with the increasing risk of rapid-succession hurricanes.
Read the full article here