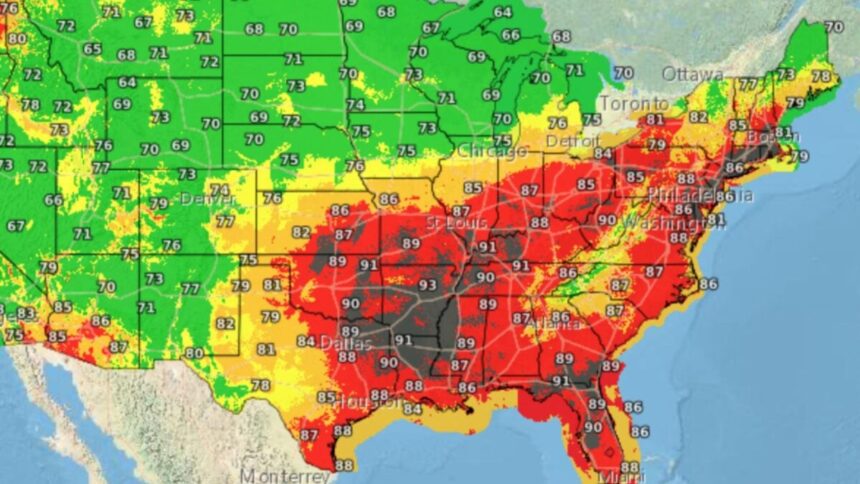
An oppressive heat dome has gripped the eastern U.S. this week, prompting the National Weather Service (NWS) to issue heat warnings for nearly 170 million Americans. To make matters worse, severe humidity is making high temperatures feel even hotter.
Extreme heat and humidity make for a deadly combination. The human body lowers its temperature by sweating, and when sweat evaporates, it cools the surface of the skin. Humidity slows this process down, increasing the risk of heat-related illness. To extrapolate the combined physiological impact of heat and humidity, meteorologists look at the wet-bulb temperature. This measurement essentially represents the amount of heat stress the body experiences under hot, humid conditions. It’s also a critical metric for understanding human survivability in a changing climate.
“The wet-bulb temperature is literally the temperature of a wet thermometer’s bulb, traditionally measured by putting a tiny wet sock on the end of a thermometer,” David Romps, a professor of Earth and planetary science at the University of California-Berkeley, told Gizmodo in an email. Similar to a sweating person, the wet-bulb thermometer cools itself by evaporating water, “but a wet-bulb thermometer is not like a person in some important ways,” he explained.
Humans generate body heat, which must dissipate into the air. “Therefore, all else equal, a sweaty person will be warmer than a wet bulb,” Romps said. When the wet-bulb temperature approaches 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 degrees Celsius)—the average human body temperature—it’s extremely difficult to maintain a safe internal temperature. This may lead to severe heat-related illness or even death, he explained.
Experts have long believed that a wet-bulb temperature of 35 degrees Celsius (equal to 95 degrees Fahrenheit at 100% humidity or 115 degrees Fahrenheit at 50% humidity) was the threshold at which the human body can no longer cool itself. In recent years, however, researchers have found evidence to suggest that this threshold is actually much lower.
“Based on our research, a wet bulb temperature of around 87 degrees Fahrenheit [30.6 degrees Celsius] at 100% humidity is the critical threshold above which humans cannot maintain a stable core temperature if they were exposed to those conditions for hours at a time,” Kat Fisher, a PhD candidate in the human thermoregulatory lab at Penn State University, told Gizmodo in an email.
Taking the wet-bulb temperature into account with air temperature, wind speed, cloud cover, and the angle of the Sun gives meteorologists the wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT), a comprehensive measure of heat stress in direct sunlight. On Tuesday, July 29, the NWS reported WBGT values in the high 80s to low 90s Fahrenheit (upper 20s to mid-30s Celsius) across much of the eastern U.S., particularly in the Southeast and Midwest.
WBGT values above 90 degrees Fahrenheit (32 degrees Celsius) are extreme and can induce heat stress in just 15 minutes when working or exercising in direct sunlight, according to the NWS. Weather officials expect these conditions to persist through Wednesday, July 29, before the heat dome dissipates later in the week.
Over the long term, dangerous wet-bulb temperature events are here to stay. “Human-caused global warming is driving up wet-bulb temperatures, pushing even healthy people closer to their physiological limit. And that limit is real,” Romps said. The human body is physiologically incapable of withstanding wet-bulb temperatures around or above its internal temperature, he explained.
As the atmosphere warms, it can hold more moisture, increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme wet-bulb temperatures. Climate models suggest that certain regions of the world could see wet-bulb temperatures regularly topping 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius) within the next 30 to 50 years, according to NASA. In the U.S., Midwestern states like Arkansas, Missouri, and Iowa will likely hit the critical wet-bulb temperature limit within 50 years.
“Throughout the 300,000 years of our species, there has been no need to tolerate such wet-bulb temperatures because it is likely they never occurred as a normal part of weather throughout that time,” Romps said. “Global warming is changing that, and fast.”
Extreme heat is already the deadliest weather hazard in the U.S. Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show that roughly 2,000 Americans die from heat-related causes per year, ABC News reports. Some experts believe the death toll is grossly underestimated. Understanding the limits of human survivability in a warmer world is literally a matter of life or death. There is an urgent need to adapt infrastructure, public health systems, and extreme heat response measures to the changing climate.
Read the full article here